The Studio Class MAID
For studio class in the summer term 2019, the students were grouped in 10 smaller groups, each group represented a specific skill, an expertise the students possessed and shared (a Tacit knowledge). We were a group of three students from India, Ann Maria Mathew, Laksha Sirohia & myself and we are experts when it comes to eating with hands. Like the unique colorful and fragrant cuisines, Indians also have unique etiquettes while dining. Eating food with hands incorporates the sense of touch which in turn provides a whole or perfect sensory experience. Our project aims to provide refined and detailed techniques on eating with hands to aid Indian food enthusiasts to enjoy Indian cuisine to the fullest extent.
How could design support the learning of an expertise from scratch by using design methods and experiments
The challenge given included, the “definition of the challenge” in actually defining what the expertise is about and how it can be learned by someone without any pre-knowledge, installing experimental learning settings supported by various design methods had been developed and tested with changing participants.
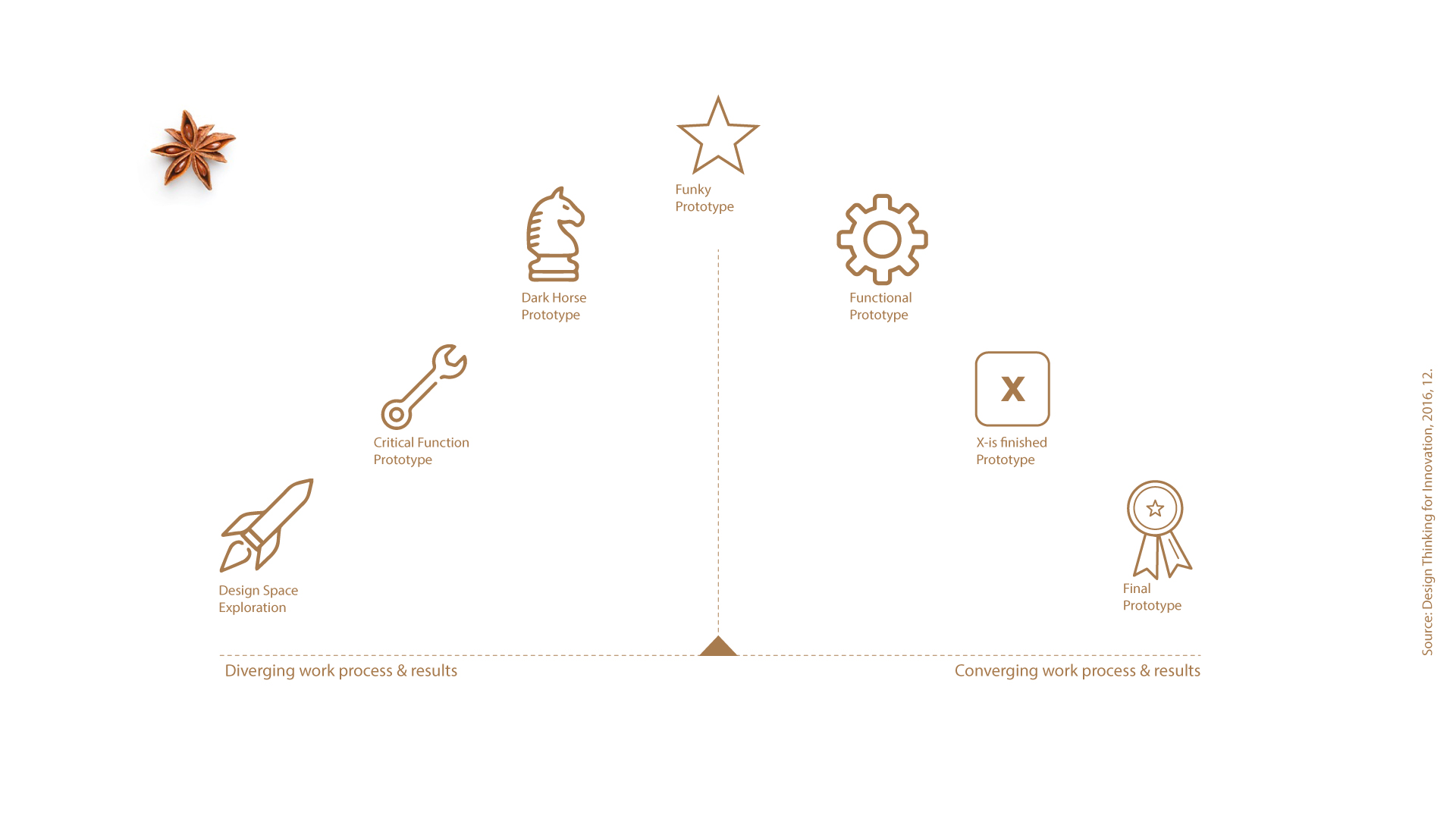

We used design thinking prototyping as an approach to develop the various experimental settings, starting from Design Space Exploration , Critical Function Prototype, Dark Horse Prototype, Funky Prototype, Functional Prototype , X-is Finished Prototype, Final Prototype. In each setting, students had to work with different participants to compare the results. In addition to the task of developing the learning setting, the experiments had to be observed and interviews had to be conducted after the experiment.
- Design Space Exploration -
“Area of subject, literature, research, talks with experts, comparing facts, competitors.”


Central Learnings
Out of the three experiments, experts teaching directly turned out to be the most effective one. Direct teaching helped participants to learn very efficiently. Experts could teach the participants directly and attend to their struggling points. Another benefit was the possibility of expert to correct the participants spontaneously. The illustrations and video tool kit helped the participants to gain some knowledge, but not effective as direct teaching. There were instances when participants failed to identify the important information. It was because these prototypes failed to give the clarity about the techniques used.

- Critical Function Prototype -
“Built on critical functions revealed in critical steps”
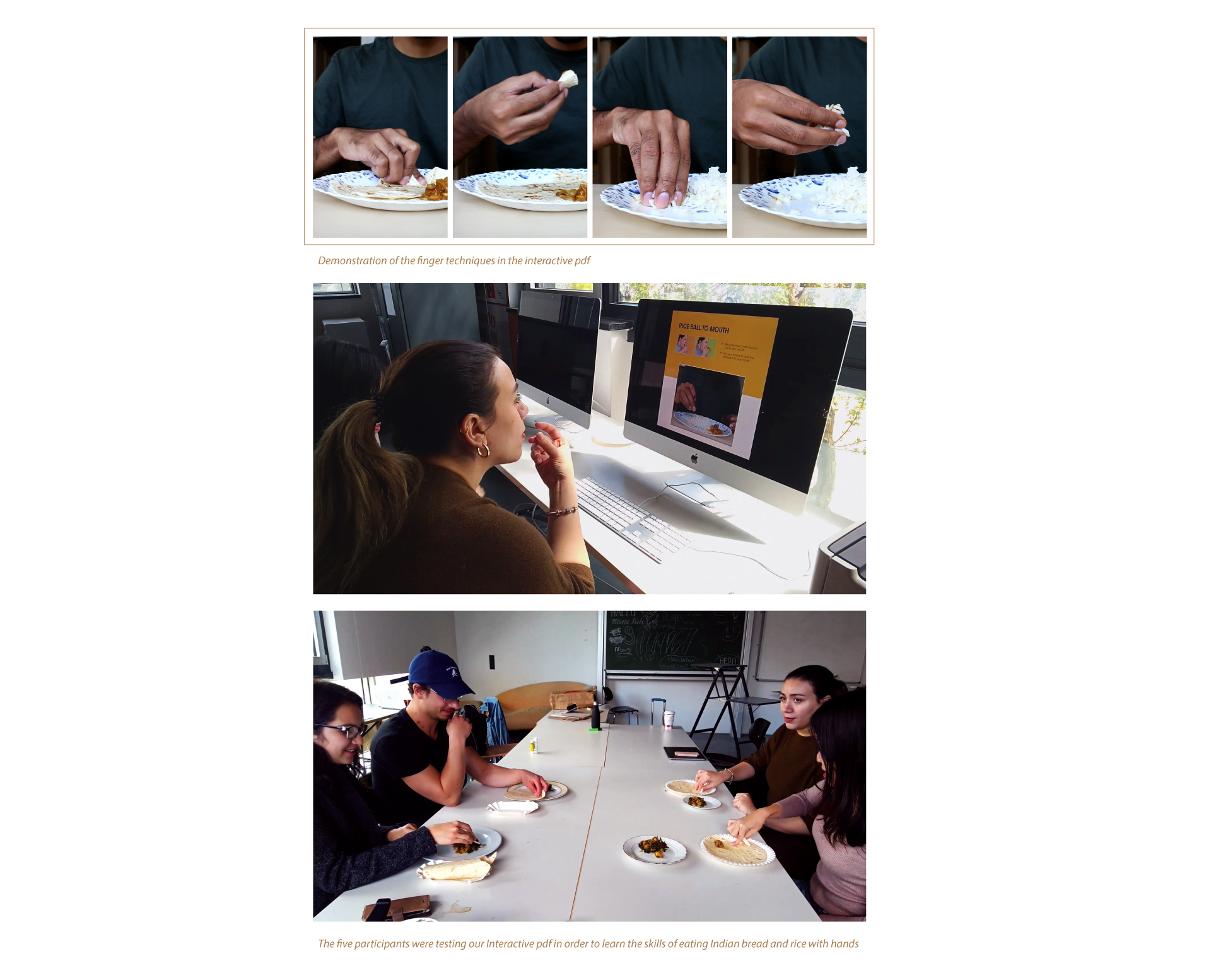

Central Learnings
Combining illustrations, video (GIFs) and instructions increased the effectiveness of the prototype. Participants were able to identify the keysteps because each steps were shown separately. They could look back and spend more time with the difficult step rather than starting from the beginning
- Dark Horse Prototype -
“Start again and get very creative and crazy.”
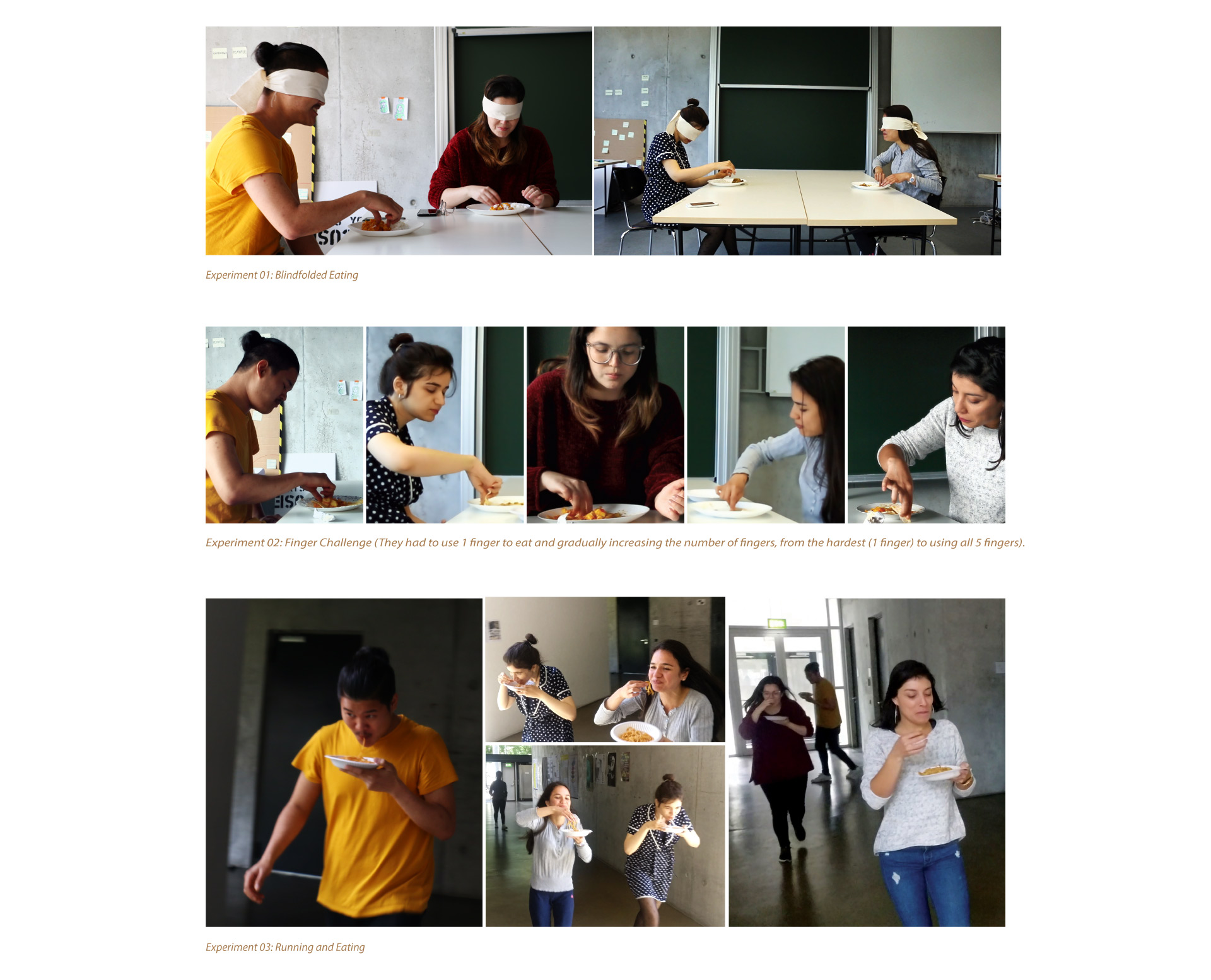

Central Learnings
Out of the three Dark Horse Experiments, expermient 02 was the most effective. The experiment started from the hardest task to being simpler, the participants gradually gained more and more confidence to tear the Roti and combine it with curry to eat. As the experiment ended there was a shocking realization that all of the participants were already using similar techniques used in India.

- Funky Prototype -
“The divergent phase is finished and all ideas will merge the best from all into one prototype.”


Central learnings:
The warm up exercise worked for the participant in this intervention. Although the warm up stage could have been for the shorter period. According to the participant, the ‘silent’ video did not have the amount of impact which a video tutorial with audio would have had. Also the participant was more interested to learn about the historical facts and stories behind the culture of eating with hands in India.
- Functional Prototype -
“Define now the details; the boundaries are fixed and defined, requirements are strictly to be followed.”
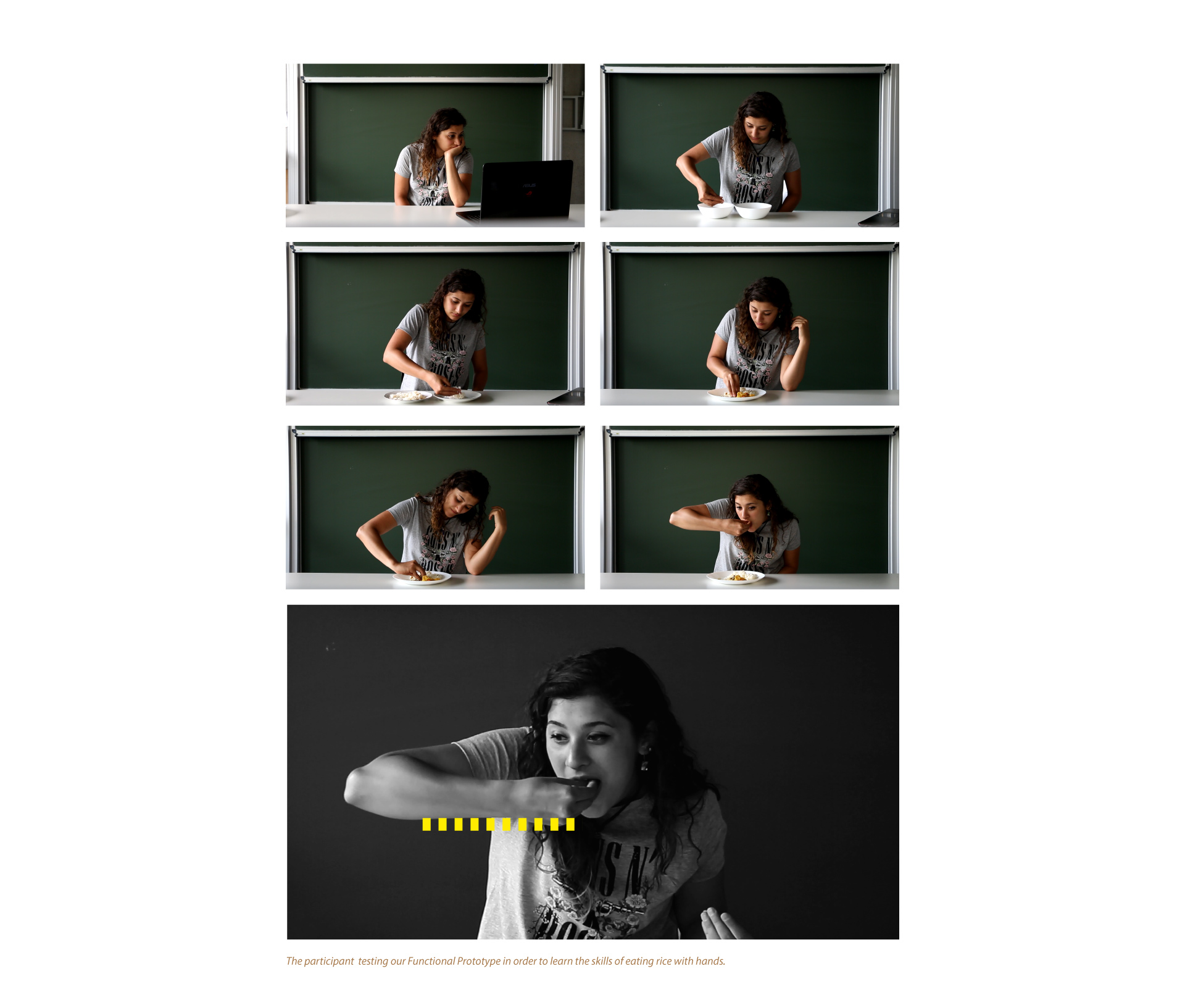


Central learnings:
The hardest element for the participant turned out to be positioning of her elbow like the experts. The video guide turned out to be very efficient in terms of translating the skills. Every person has a different way of learning the same task given to him/her. In this Prototype stage our participant’s personality helped her to learn quickly. She being an enthusiastic fast learner and ready to take up challenges with a love for exploring cultures made her learn the techniques efficiently.
- X-is finished Prototype -
“One key functionality (x) needs to be explored and it helps to disregard ununrealistic components.”


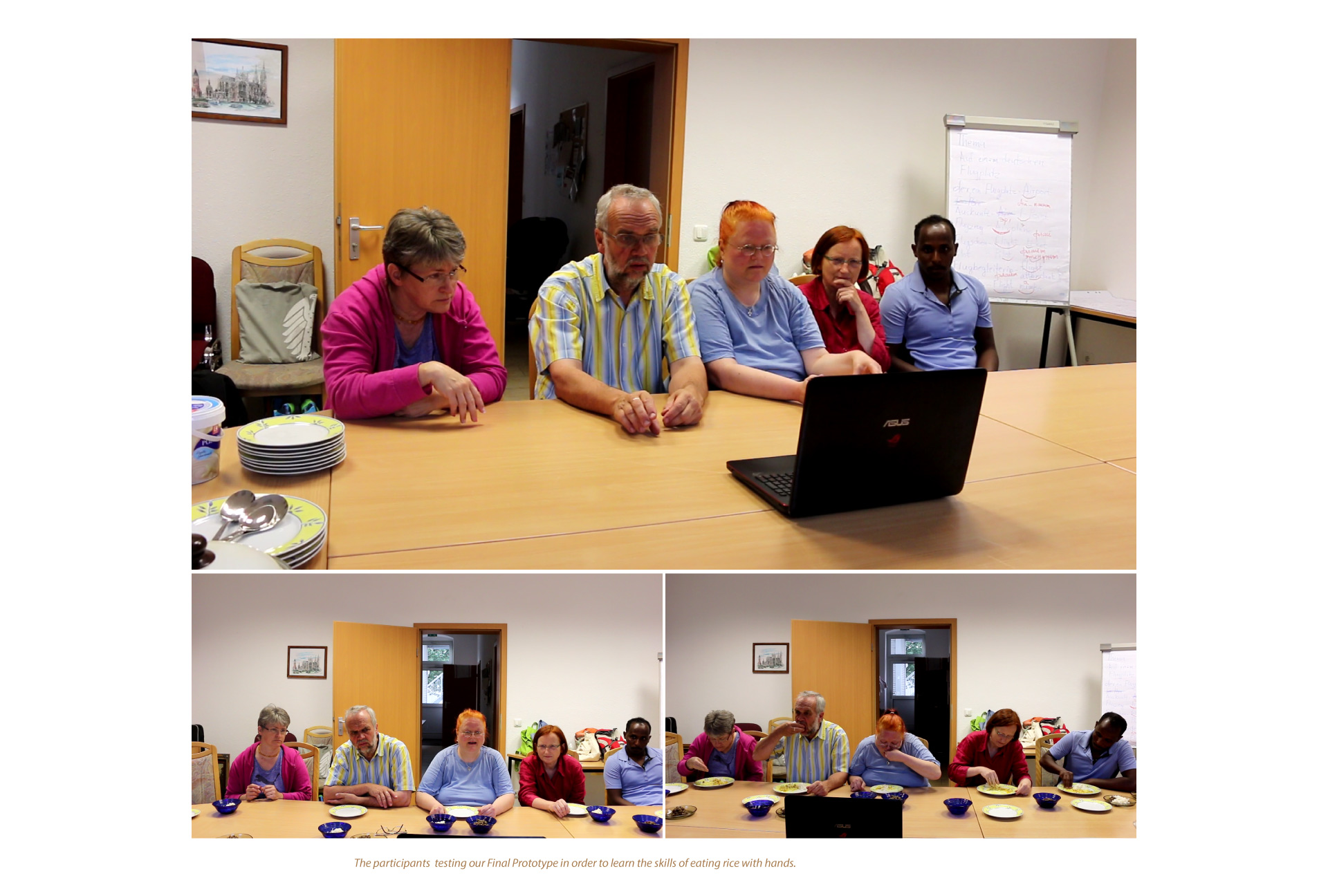
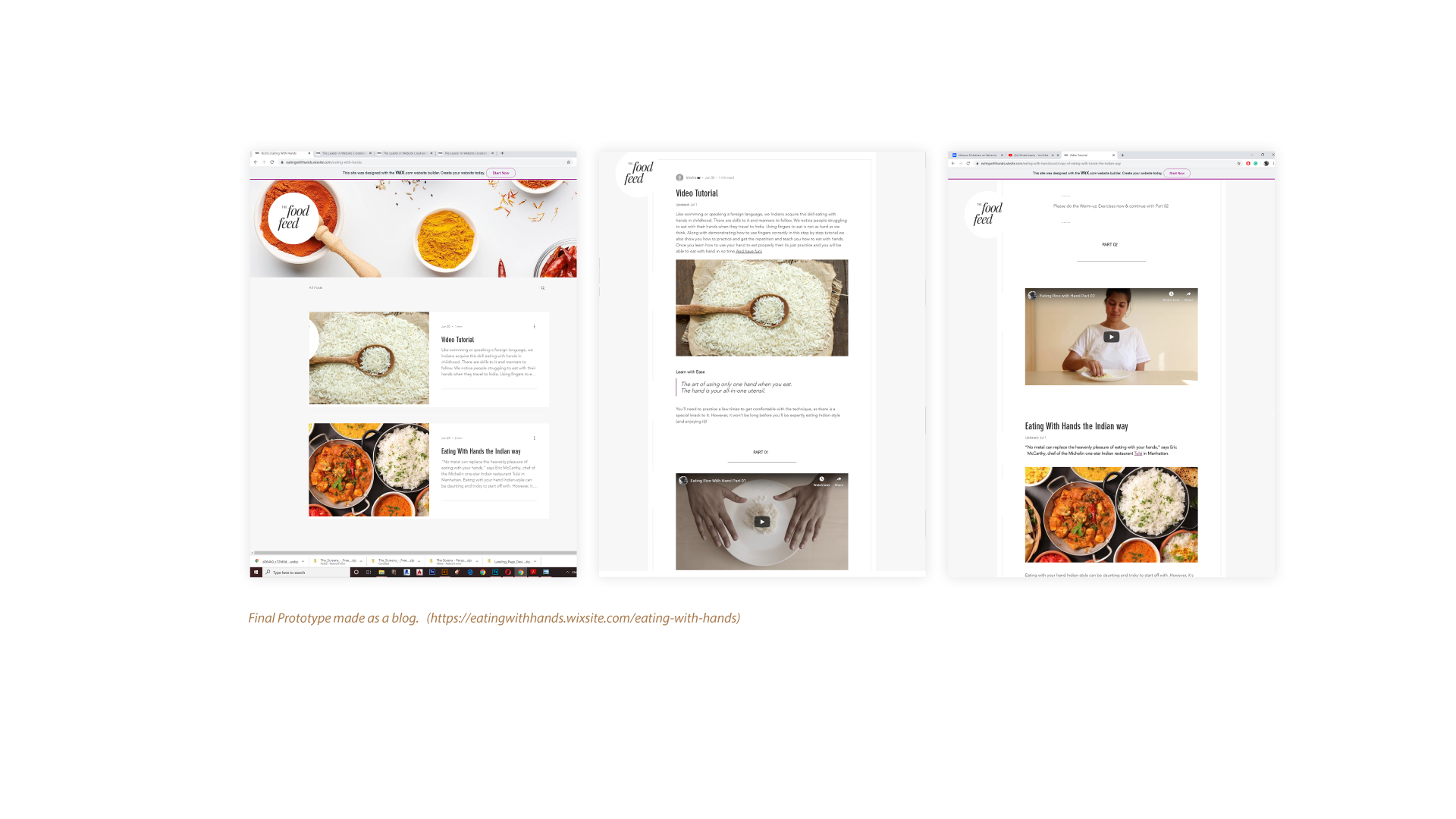
- Final Prototype -
“Comprises all functions to satisfy realizable customer needs”


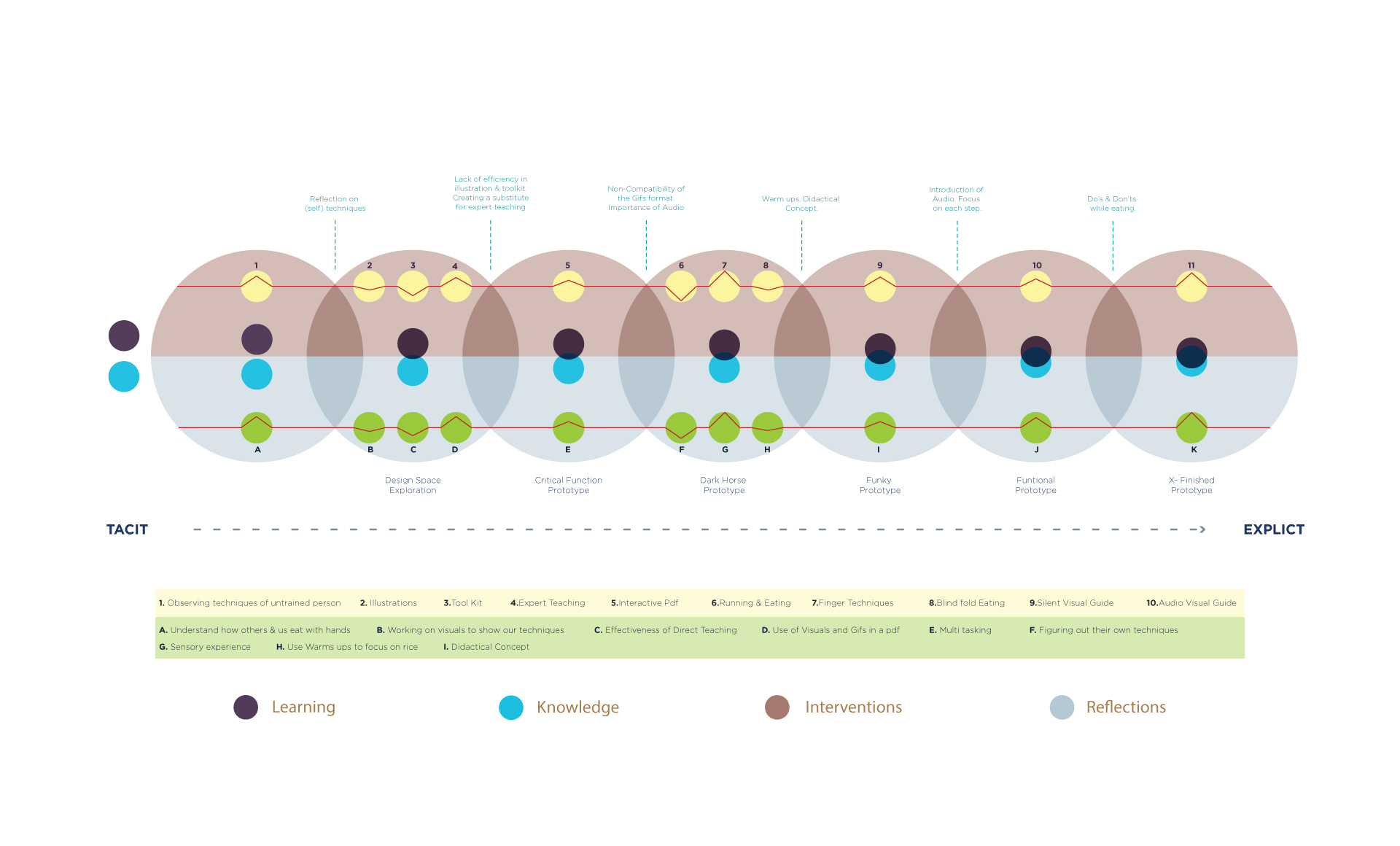
- Diagram showing the whole process -

Selected Works

SAP GraphUX/UI

MaynoothUI/UX

GraphGraphic Design

MiriaMansonGraphic Design

RageofashionBranding

KPx Brennende FragenMovie // Motion Graphics